|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Composite Materials |
||||||||||||||||||
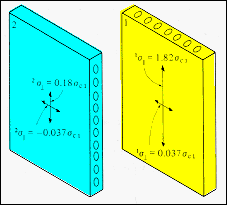
· The layers of a laminate interact
to produce complex stress distributions when the composite is simply loaded. |
||||||||||||||||||
· Due to this stress and constraints
from lamina 2, lamina 1 sees a tensile stress in the parallel direction, 1σ1
= 1.82 σ1C , and a
tensile stress normal to the fibers, 1σ2 = 0.037 σ1C . |
||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||
From:
Hull, |
||||||||||||||||||