|
Stainless
Steel
·
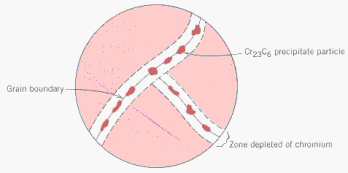
Heat
treatment of a stainless steel during fabrication can also alter its resistance
to corrosion as a result of the changed distribution of chromium in the
alloy. This is illustrated below for a grain-boundary region in which chromium
carbide particles have been precipitated, removing chromium from the grain
boundary region, and making it susceptible to corrosion.
·
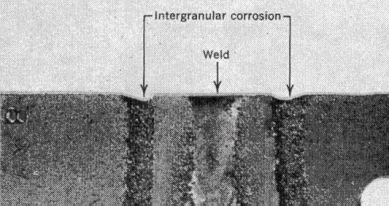
The
photograph shows a fusion weld between two stainless steel plates. The
steel melts at this joint and alloying elements are redistributed in the
cooling process. Change in the chromium content close to the weld permits
intergranular corrosion to occur in this region, the rest of the material
being passivated under the same corrosion conditions. The carbide particles,
Cr23C6, that remove Cr from the matrix are not attacked
in the corrosion reaction. |