|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Failure Mechanisms |
|||||||||||||||
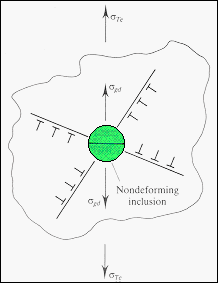
· Void formation occurs under
the maximum values of the tensile and shear stresses at the center of the sample. |
|||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||
From:
Courtney, "Mechanical Behavior of Materials," McGraw Hill (1990) |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Failure Mechanisms |
|||||||||||||||
· Void formation occurs under
the maximum values of the tensile and shear stresses at the center of the sample. |
|||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||
From:
Courtney, "Mechanical Behavior of Materials," McGraw Hill (1990) |
|||||||||||||||