|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Failure Mechanisms |
|||||||||||||||||
Fatigue · Fatigue failure results from the periodic application of a stress that may be less than the material's yield stress. |
|||||||||||||||||
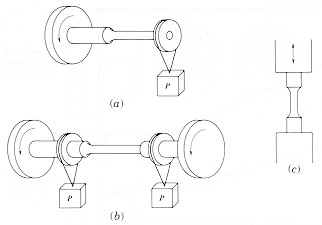
· Some fatigue
test configurations
are illustrated. (a) Single point loading: the bending
moment increases towards
the "fixed" end; (b) Pure bending with a constant bending moment
over the test section; (c) Uniaxial loading with periodic tension/tension
or tension /compression cycles. |
|||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
From:
Hertzberg, Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, Wiley
(1989) |
|||||||||||||||||