| |
· Turbine blades experience high
tensile loading due to the engine rotation. Aerodynamic clearances need
to be low, and creep is a major factor in blade life.
· High melting point metals are needed to reduce the
effects of creep which depend on the reduced temperature (T/Tm).
Nickel
based alloys are used for current turbine blades.
· The control of alloy composition and microstructure
is essential to obtaining optimum performance.
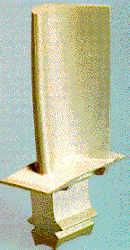
· The uniaxially solidified 'single
crystal' turbine
blade shown is an early example from Pratt and Whitney.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|