|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Composite Materials | |||||||||||||||||
| ·
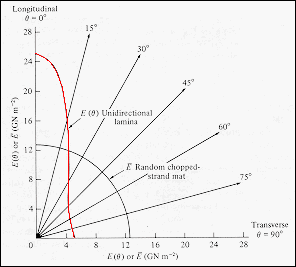
When
a composite is tested with the fibers at different angles to the tensile
axis the elastic modulus will lie
between the parallel and orthogonal values.
· The orientation dependence of the Young's modulus for a glass-fiber polyester resin composite with Vf = 0.30 is shown (red curve). For the system, Em = 3.5 GPa, Ef = 76 GPa, and Vm = 0.7. · The second curve (black) represents a composite with short, randomly oriented fibers. This material is isotropic in its elastic modulus. |
|||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| From:
Hull,
"Introduction to Composite Materials," Cambridge (1992) |
|||||||||||||||||