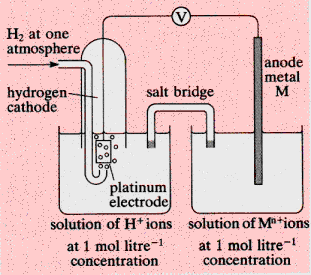
|
Electrode
Potentials
·
A metal in a steady state with a solution containing
ions of the metal has a potential difference, the contact potential or
electrode potential, between it and the solution.
·
The
contact potential cannot be measured with a single reversible electrode,
and the circuit shown in the diagram is used. A hydrogen cathode serves
as the standard reference electrode and is assigned zero Volts.
·
The system is a "battery" and its voltage, V, can
be used to characterize the standard electrode potential of the metal
with respect to the reference hydrogen electrode.
· This
contact potential depends upon temperature, pressure, and the ionic concentration
of the solutions. Molar solutions, containing one mole of the ions per
litre of solution, with measurements made at STP, establish the reference
condition. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|