|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Failure Mechanisms |
||||||||||||||||||||||
· Fracture modes are dependent upon strain rate, homologous temperature (T/Tm), and the material crystallography and microstructure. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
From:
Courtney, "Mechanical Behavior of Materials," McGraw Hill (1990) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
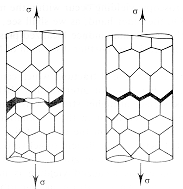
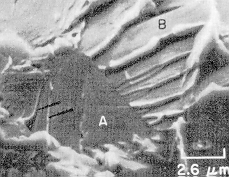
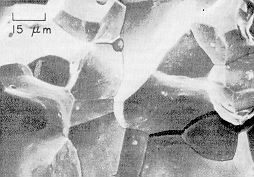
· A brittle material fails by rapid crack propagation normal to the tensile axis. In a technical material the crack may propagate through the grains (trans-granular fracture) or along grain boundaries (inter-granular fracture) as illustrated for carbon steel and Armco steel with oxidized grain boundaries. |
||||||||||||||||||||||